Page History: Fourier Transform Properties
Compare Page Revisions
Page Revision: 2010/11/11 16:06
Fourier Transform Properties - Separability
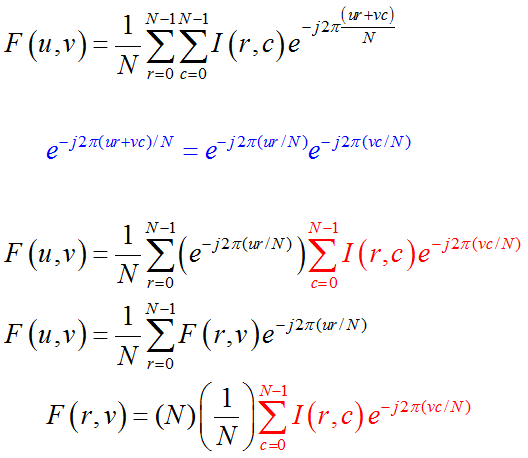
Fourier Transform Properties - Convolution
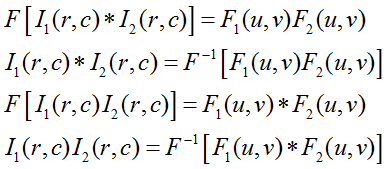
Fourier Transform Properties - Translation
Translation property results in a phase shift of the spectrum. (a) Original
image. (b) The magnitude of the Fourier spectrum from (a) represented as an
image. (c) The phase of the Fourier spectrum from (a) represented by an image.
(d) and (g) are original image shifted by 128 rows and 128 columns, and 64 rows
and 64 columns, respectively. (e), (h) The magnitude spectrum. (f), (i) Phase
spectrum. These images illustrate that when an image is translated, the phase
changes, even though magnitude remains the same.
Fourier Transform Properties - Rotation
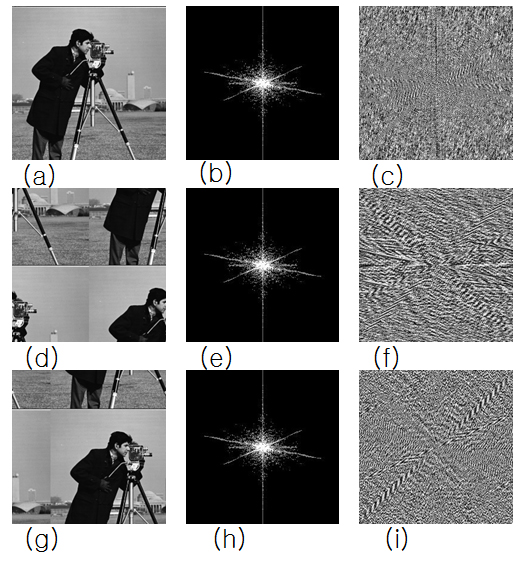
Translation property results in corresponding rotations with image and
spectrum. (a) Original image. (b) Fourier spectrum image of original image. (c)
Original image rotated by 90 degrees. (d) Fourier spectrum image of rotated
Fourier Transform Properties – Periodicity
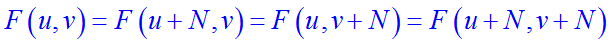
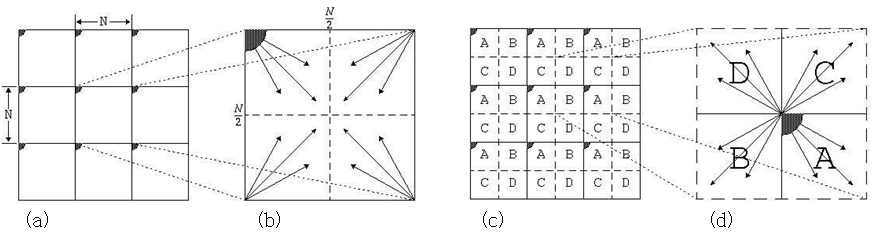
Periodicity and implied symmetry for the Fourier transform. (a) Implied symmetry with origin in upper-left corner. Each NxN block represented all the transform coefficients, and is repeated infinitely in all directions. (b) Increasing frequency in direction of arrows. (c) Periodic spectrum, with quadrants labeled A, B, C, and D. (d) Spectrum shifted to center. Frequency increases in all directions as we move away from the
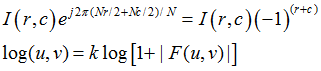

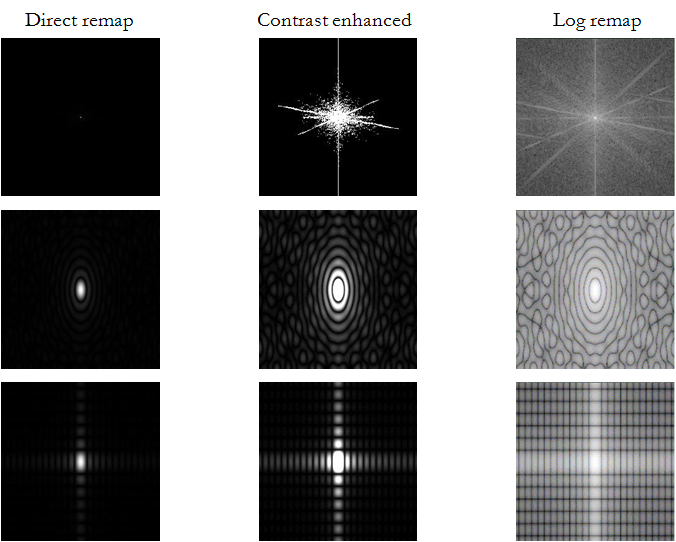
Directing mapping of Fourier magnitude data. (a) Original image. (b) The Fourier magnitude directly remapped to 0-255 without any enhancement. (c)-(e) Contrast enhanced versions of (b).
Discrete Fourier Transform Program Coding
1. input image : own created image with proper size
2. program code must be your own
3. Discuss result
□ image -> DFT -> log scale transform -> Display
left : original input image
middle : normal display of FFT transform
right image : log display of FFT transform
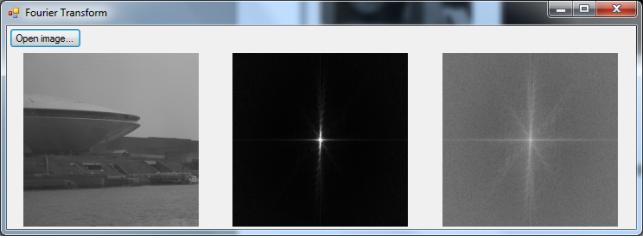
■ created image : 512×512 image
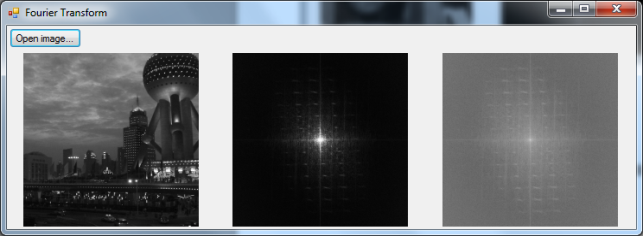
■ created image : 1024×1024 image
Source
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
minMagnitude = Math.Min(minMagnitude, data
y,x.Magnitude);
maxMagnitude = Math.Max(maxMagnitude, data
y,x.Magnitude);
minLog = Math.Min(minLog, Math.Log(data
y, x.Magnitude));
maxLog = Math.Max(maxLog, Math.Log(data
y, x.Magnitude));
}
}
// do the job
unsafe
{
byte* dst = (byte*)dstData.Scan0.ToPointer();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++, dst++)
{
if (logTransform)
*dst = (byte)System.Math.Max(0, System.Math.Min(255, (Math.Log(data
y, x.Magnitude) - minLog) * 255 / (maxLog - minLog
;
else
*dst = (byte)System.Math.Max(0, System.Math.Min(255, data
y, x.Magnitude * scale * 255));
}
dst += offset;
}
}
)))